AO-PI Viability Assay
The Acridine Orange (AO) / Propidium Iodide (PI) assay is used for cell counting and viability. AO is a nucleic acid-binding fluorophore that is cell membrane permeable and suitable for selective staining of nucleated cells. PI is a nucleic acid-binding dye that is impermeable to live cells and suitable for staining dead, nucleated cells. All live, nucleated cells fluoresce green due to AO, while dead, nucleated cells are stained with both AO and PI and fluoresce red.
Acridine Orange
The Acridine Orange (AO) Dye is used for total cell counting. AO is a nucleic acid-binding fluorophore that is cell membrane permeable and suitable for selective staining of nucleated cells.
Propidium Iodide
The Propidium Iodide (PI) Dye is used for viability assessment. PI is a nucleic acid-binding dye that is impermeable to live cells and suitable for staining dead, nucleated cells.
Yeast
The Fluorescein Diacetate (FDA) and Propidium Iodide (PI) assay is used for yeast cell viability testing. FDA is a cell viability probe that is membrane-permeable to live yeast cells. Inside a live cell, FDA is cleaved to give fluorescein by the action of intracellular esterases. Propidium Iodide dye for viability assessment. PI is a nucleic acid-binding dye that is impermeable to live cells and suitable for staining dead, nucleated cells. Live cells are reported by FDA in the green channel, dead cells by PI in the red channel.
Trypan Blue
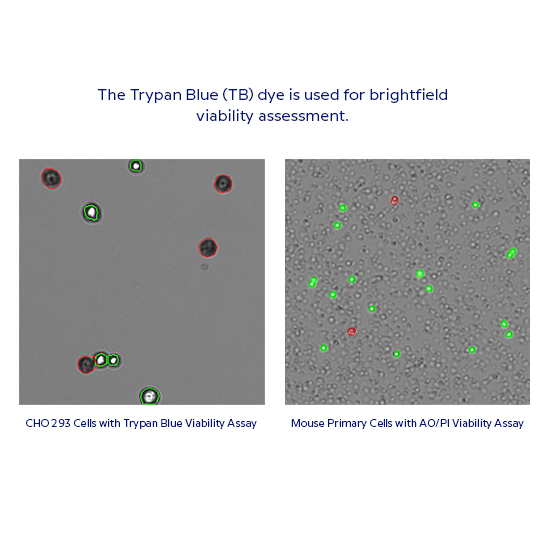
The Trypan Blue (TB) dye is used for brightfield viability assessment. TB is an azo dye that is excluded from cells with intact cell membranes, only staining non-viable cells. The trypan blue assay is used to assess the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension.
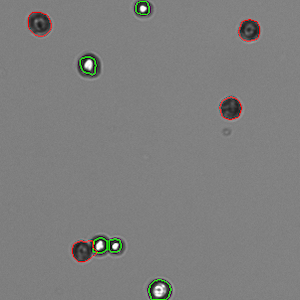
CHO 293 Cells with Trypan Blue Viability Assay
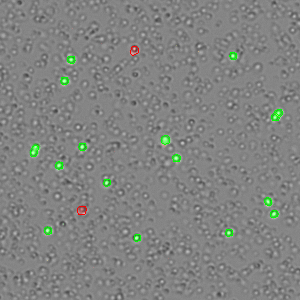
Mouse Primary Cells with AO/PI Viability Assay

 English
English